Did you know that planning your meals can help you avoid overeating? It can also manage hunger and mood swings. Audra Wilson, MS, RDN, CSOWM, CSCS, says that when you eat is just as important as what you eat. Eating at set times can control your appetite, increase your energy, and help with weight management.
We will look into why meal timing is so important. We’ll also give tips on how to plan your meals and snacks for the day. This will consider different ages and their unique needs for the best eating schedule.
Key Takeaways
- Eating at regular intervals helps regulate appetite and boost energy levels, which is essential for a better health eating schedule.
- Ideal meal times vary by age group, and understanding these differences is key for meal timing matters.
- A consistent eating schedule supports weight management and overall well-being, making ideal meal times a key factor.
- Meal timing affects digestion, with regular timing promoting regular digestive patterns and a better health eating schedule.
- Eating a high-protein breakfast and having substantive meals every four hours can help prevent blood sugar level dips and support meal timing matters.
- Stopping eating between dinner and breakfast can lead to weight loss and better sleep quality, highlighting the importance of ideal meal times.
- Understanding the science behind meal timing is essential for creating a personalized meal plan that suits individual needs and promotes a better health eating schedule.
Understanding the Science Behind Meal Timing
Exploring meal timing means diving into the science behind it. Our bodies have an internal clock that controls digestion and metabolism. This clock is set by circadian rhythms, which cycle every 24 hours. Studies show that our ability to control hunger is tied to these rhythms.
To optimize eating times and boost health, we must consider how meal timing impacts our hormones, metabolism, and digestion.
When deciding when to eat for health, age is a key factor. Children and teens have different nutritional needs than adults or seniors. By planning meals based on these needs, we can optimize eating times and enhance our well-being. A well-thought-out meal schedule can help manage hunger, increase energy, and support health.
To achieve meal timing for wellness, we must consider our unique needs and lifestyles. This includes our daily routines, health conditions, and activity levels. By planning meals that fit our individual needs, we can create a personalized schedule that supports our health and well-being. Whether we aim to boost energy, improve digestion, or feel our best, understanding meal timing science is key.
Circadian Rhythms and Digestion
Our circadian rhythms are vital for digestion and metabolism. Eating in sync with these rhythms can greatly benefit our health. By grasping how our internal clock influences our body, we can make better meal timing choices and support our well-being.
The Perfect Morning Meal Schedule
Eating breakfast is key to keeping our energy up and staying healthy. The timing of our meals, like breakfast, really matters. Studies say eating breakfast soon after waking helps kickstart our day with the right fuel.
Breakfast is more important for kids as it helps them grow. Sadly, many kids skip breakfast. This can harm their insulin levels and how they react to food later.
Starting the day with a healthy breakfast can help us stay slim. It’s linked to a lower BMI and better weight control. Here are some perks of breakfast:
- Improved brain function, memory, attention, and performance on various academic tasks
- Better weight loss compared to eating larger meals in the evening
- Lower risk of metabolic conditions such as high blood sugar, increased blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat
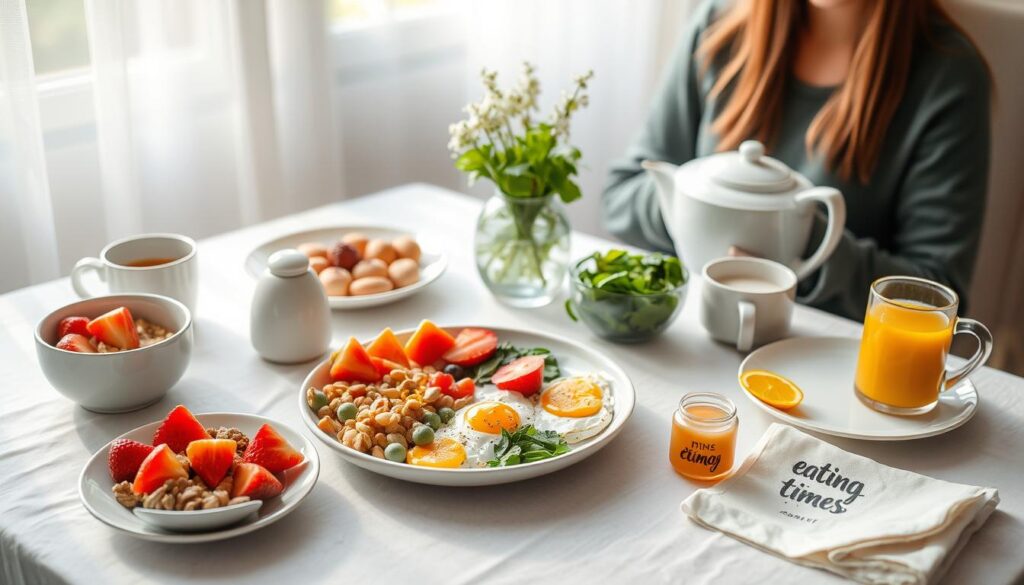

In short, a good morning meal schedule is vital for our energy and health. Knowing the best times to eat and the benefits of meal timing helps us make better food choices.
| Age Group | Breakfast Importance | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Children | High | Supports growth and development, improves brain function and memory |
| Adolescents | High | Supports growth and development, improves brain function and memory, reduces risk of metabolic conditions |
| Adults | Moderate | Supports weight loss, improves brain function and memory, reduces risk of metabolic conditions |
Optimal Lunch Timing for Maximum Energy
Lunch is key for boosting energy and health. Eating early can help with weight loss and lower disease risks. The right meal times are vital for health.
Adults should eat lunch between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. This matches our body’s peak energy time. A balanced meal with protein, fat, and fiber keeps us full and avoids snacking.
- Eating smaller portions closer together throughout the day for individuals with digestive disorders
- Maintaining blood sugar levels by spacing meals around 4-6 hours apart
- Consuming meals slowly and mindfully to feel fuller for longer
Understanding meal timing is important. By adjusting our eating and exercise, we can improve our health. This leads to better overall well-being.
Evening Eating: Finding Your Ideal Dinner Window
Dinner is key for unwinding and recharging after a long day. Eating a balanced dinner early in the evening can help with weight loss and better health. It also lowers the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Studies show that eating between 5 P.M. and 7 P.M. is best for weight management. A 2022 study in Cell Metabolism found that those who eat at 5 P.M. burn 60 more calories than those at 9 P.M. Early dinner also helps keep blood sugar stable, boosts metabolism, and may prevent weight gain.
Here are some tips for finding your ideal dinner window:
- Eat dinner at least two to three hours before bed to avoid stomach discomfort.
- Wait three to four hours between meals or snacks for stable blood sugar.
- Choose nutrient-dense foods like whole grains, fruits, lean proteins, and veggies.

By following these tips, you can find your perfect dinner time. Remember, meal timing for health is very important. Eating a balanced dinner early can greatly improve your well-being.
| Meal Timing | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Eating dinner between 5 P.M. and 7 P.M. | Supports weight loss, improves overall health, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases |
| Eating dinner earlier | Stabilizes blood glucose levels, boosts metabolism, and potentially lowers the chance of weight gain |
Age-Specific Meal Timing Guidelines
Different ages have different nutritional needs. It’s important to consider these when planning meals. This includes children, teenagers, adults, and seniors.
Children and teenagers need balanced meals for growth. The USDA offers healthy eating patterns for everyone. These patterns help ensure we get the right nutrients.
Children and Teenagers (Ages 5-18)
Kids might need to try new foods 10-15 times before liking them. Toddlers should have 4-8 servings of vegetables daily. Preschoolers need 3-4 servings, and elementary school kids should have 2-4 servings.
Adults (Ages 19-50)
Adults should eat a variety of foods to stay healthy. The USDA MyPlate Kitchen has recipes for everyone. It helps create food plans based on age, height, weight, and activity level.
Seniors (Ages 51+)
Seniors should focus on healthy eating. Caloric needs vary, so talk to a healthcare provider before changing diets.
By considering age-specific needs and following healthy patterns, we can create good eating schedules. Stay hydrated, limit sugary foods, and choose whole, nutrient-rich foods.
| Age Group | Recommended Servings of Vegetables | Recommended Servings of Dairy | Recommended Servings of Protein |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toddlers (1-3 years) | 4-8 servings per day | 4-5 servings per day | 2-5 servings per day |
| Preschoolers (4-5 years) | 3-4 servings per day | 3-5 servings per day | 3-5 servings per day |
| Elementary school-age children (6-12 years) | 2-4 servings per day | 3 servings per day | 2-3 servings per day |
Meal Timing for Weight Management and Better Health
Research shows that eating at certain times can help with weight loss and better health. It can also lower the risk of diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. The timing of meals is key because it affects our body’s natural rhythms and how it uses energy.
Eating earlier in the day can bring many health benefits. For example, a study found that eating half of your daily calories at breakfast can lead to more weight loss than eating the same amount at dinner. This was over a 12-week period.
Here are some key findings related to meal timing and health:
- Late lunch eaters (after 3 p.m.) lost less weight during treatment compared to early lunch eaters (before 3 p.m.)
- Eating the largest meal in the morning results in better sleep patterns and improved metabolic rate
- Shifting most caloric intake to earlier in the day can benefit metabolic health

By using these findings in our daily routines, we can improve our meal timing and health for better weight management and overall well-being. It’s important to think about our personal preferences, schedules, and health goals when deciding when to eat.
| Meal Timing Strategy | Health Benefits |
|---|---|
| Time-restricted eating | Weight loss, improved metabolic health |
| Front-loading calories at breakfast | Improved appetite control, blood sugar balance |
| Eating earlier in the day | Better sleep patterns, improved metabolic rate |
Special Considerations for Different Lifestyles
Meal timing varies for different lifestyles. Night shift workers, for example, need to adjust their eating to fit their work hours. They can eat smaller meals often during the night instead of big meals at odd times.
Athletes and those who are active need a special eating plan. They should eat a meal with protein, carbs, and fats 1-2 hours before working out. Then, they should eat carbs and protein within 30-60 minutes after to help recover.
Busy professionals also benefit from a good eating plan. Eating healthy meals and snacks helps keep their energy up. It’s important to think about meal timing to improve health.
Some key things to consider for different lifestyles include:
- Eating frequent, balanced meals to support energy needs
- Avoiding large meals close to bedtime
- Incorporating physical activity into daily routines
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
By planning meals that fit their lifestyle, people can enjoy the health benefits of meal timing. This supports their overall well-being.
The Impact of Meal Spacing on Digestion
Eating at regular times can help our digestion and health. It also lowers the risk of diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. To do this, we should eat at the best times and follow meal timing tips.
Eating regularly tells our body it has enough food, which is key for health. It’s good to eat within 2 hours of waking up to fuel our body. Most people need to eat again every 3-4 hours, based on what they eat.
Optimal Time Between Meals
A balanced meal with protein, fiber, veggies, fruits, and fats keeps us full longer. Eating at the same times helps our body know when to feel hungry. It’s best to have meals 4 to 6 hours apart to keep our small intestine clean.

Managing Snacks and Small Meals
Only 40% of people stick to three meals a day. Some mix meal spacing with fasting, skipping food for 12-16 hours. But, people with diabetes might need to eat more often. Knowing the best times to eat and following meal tips helps us make better choices for our health.
Adapting Your Meal Schedule to Your Natural Rhythm
As we get older, our bodies change in many ways. This affects how we eat and when we eat. Adults with busy lives need balanced meals to keep their energy up. Studies show eating later in the day can lead to health problems, showing how important eating schedule importance is.
Planning our meals well is key to staying healthy. Eating at regular times helps our body digest food better. The American Heart Association says eating mindfully can lead to a healthier life and better heart health.
Here are some tips for adjusting our meal times to our natural rhythm:
- Eating a big breakfast and a small dinner can help with weight loss and better health
- Avoid eating close to bedtime to avoid weight gain and health issues
- Listen to our body’s hunger signals and adjust our meal times
By following these tips, we can make our eating schedule better. It’s important to remember that everyone is different. We need to find a meal schedule that fits our unique needs.
Common Meal Timing Mistakes to Avoid
When it comes to meal timing, avoiding common mistakes is key for good health. Eating dinner early, 2-3 hours before bed, helps with weight loss. It also matches our natural body rhythms. Eating most of our calories by mid-afternoon also aids in weight management.
We often eat too much because of bad habits like eating fast or finishing our plates. In fact, 80% of people overeat because of these habits. To avoid this, planning meals and eating mindfully is important. This helps us know when we’re full, not stuffed.
Some key mistakes to avoid include:
- Late-night eating, which can disrupt digestion and lead to weight gain
- Irregular eating patterns, which can confuse the body’s natural rhythms
- Skipping meals, which can lead to overeating or poor food choices
By avoiding these mistakes and focusing on the benefits of meal timing, we can improve our health. For instance, eating dinner at 5 p.m. instead of 8 p.m. can help our body rhythms and aid in weight loss. Making smart choices about when we eat can help us control our health and enjoy a balanced diet.
The secret to good meal timing is finding a rhythm that suits us and sticking to it. By doing this, we can enjoy the benefits of meal timing and make it a regular part of our lives.
| Meal Timing Mistake | Health Impact |
|---|---|
| Late-night eating | Disrupts digestion, leads to weight gain |
| Irregular eating patterns | Confuses body’s natural rhythms |
| Skipping meals | Leads to overeating or poor food choices |
Creating Your Personalized Meal Timeline
Creating a meal timeline can boost your health and lower disease risks. It’s key to think about meal timing tips and make an eating schedule that fits your life and age.
Adults need balanced meals to keep up with their busy lives. A meal with grilled chicken, veggies, and whole-wheat tortilla is great. It’s under 750 calories and adds to your veggie intake.
Here are some meal timing tips for your eating schedule:
- Eat within two hours of waking up
- Have meals every three to four hours
- Stop eating at least three hours before bedtime
Having fruits, veggies, whole grains, and beans on hand can encourage more eating of them. Meal planning saves time and money by buying in bulk.

By using these meal timing tips and making a personalized eating schedule, you can improve your health. Always talk to a doctor to make sure your meal plan is right for you.
| Age Group | Meal Timing Tips |
|---|---|
| Adults | Eat within two hours of waking up, have meals every three to four hours |
| Seniors | Consider earlier dinner times, avoid eating at least three hours before bedtime |
Conclusion: Making Meal Timing Work for Your Health
Meal timing matters a lot for our health and happiness. By learning about our body’s natural rhythms, we can plan the best times to eat. This is true for everyone, whether you’re busy, active, or enjoying retirement.
Research shows that eating at the right times can boost energy and help with weight. It can also lower the risk of serious diseases. By eating wisely, we improve how our body absorbs nutrients and perform better.
It’s important to try different meal times to see what works for you. By finding the right schedule, you can improve your health. This is all about finding the best meal timing for you.
FAQ
What is the importance of meal timing for our overall health and well-being?
Meal timing is key to our daily health. It helps control hunger, boosts energy, and aids in weight management.
How do circadian rhythms and other physiological processes affect meal timing?
Our body’s natural rhythms guide digestion and metabolism. Eating in sync with these rhythms boosts health. Meal timing also influences hormones and metabolism.
What are the benefits of starting the day with a nutritious breakfast?
Breakfast is vital for energy and health. It keeps us energized and supports our overall well-being.
How can the timing of our lunch affect our energy levels and productivity?
Lunch boosts energy and supports health. An early lunch can prevent afternoon slumps and boost productivity.
What is the ideal dinner window, and how can it impact our overall well-being?
Dinner helps us relax and recharge. Finding the right dinner time supports our health and well-being.
How do the nutritional needs and meal timing requirements differ for different age groups?
Meal timing varies by age. Children, teens, adults, and seniors have unique needs. Each group requires specific meal timing and nutrition.
How can meal timing support weight management and overall health?
Meal timing aids in weight control and health. Strategies like time-restricted eating offer benefits for weight management and overall well-being.
What are the unique meal timing considerations for different lifestyles, such as night shift workers, athletes, and busy professionals?
Various lifestyles need unique meal timing plans. Night shift workers, athletes, and busy professionals have specific needs. These must be addressed for their health and well-being.
How does meal spacing impact our digestion and overall health?
Meal spacing affects digestion and health. Optimal meal intervals and snack management support digestive health and overall well-being.
How can we adapt our meal schedule to our natural rhythm and support our overall health?
Adapting meals to our natural rhythm supports health. Listening to hunger cues and adjusting meal times benefits our health and well-being.
What are some common meal timing mistakes to avoid?
Avoid late-night eating, irregular patterns, and skipping meals. These mistakes harm health and well-being.
How can we create a personalized meal timeline to support our overall health and well-being?
A personalized meal timeline involves planning meals and snacks. It addresses age and lifestyle needs, supporting health and well-being.



